Does Choice Theory or Routine Activities Theory Describe Delquncy Best
The theory of rational choice theory examines offender decision making and the factors that affect it such as assessments of risks rewards and morality of various behaviors Clarke 1983. The risk level is the first factor taken into consideration when determining whether a target is good.
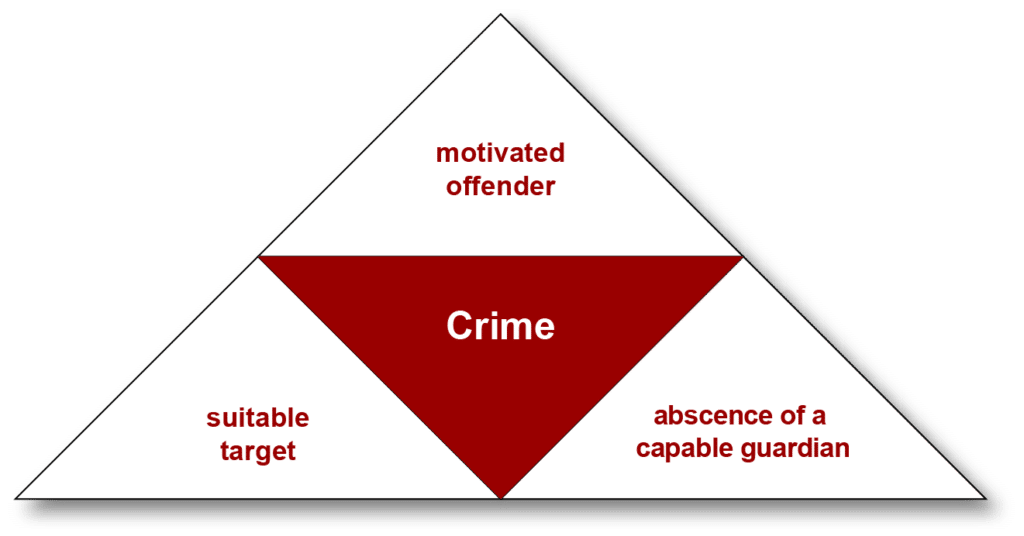
Routine Activity Theory Rat Soztheo
The absence of capable guardians that could intervene 3.

. Routine activities theory has guided research designed to understand a range of phenomena including crime trends over time distributions of crime across space and individual differences in victimization. Secondly there is a suitable target and finally there is an absent capable guardian. Routine activities theory is a theory of crime events.
The theory has three assumptions. Routine activity theory is a sub-field of crime opportunity theory that focuses on situations of crimes. Risk and rewards heavily effects an offenders decision of a target Clarke1983.
The balance between likely risks and rewards influences offenders target selection Clarke 1983. -Best way to convictswiftcertain severe punishment. Choice Theory routine activity Rational choice theory commonly known as choice theory is based off of beliefs from classic criminology which believe that individuals freely choose their behavior and are motivated by the pursuit of gratification and the attempt to avoid pain Read More Juvenile Delinquency Is An Example Of Deviant Behavior.
Routine Activity Theory focuses on situations of crime. Siegel Welsh 2008 define Juvenile delinquency as participation in. This differs from a majority of criminological theories which focus on explaining why some people commit crimesthat is the motivation to commit crime rather than how criminal events are produced.
However rational choice recognizes that some behavior is spontaneous result - ing from past experience and the routine of daily life. A motivated offender with criminal intentions and the ability to act on these inclinations a suitable victim or target and the absence of a capable guardian who can prevent the crime. Trait theory supports that an individuals choice is actually the product of a physical or psychological abnormality or defect.
First there is a motivated offender. Deterrence Theory popular in 1970s -Based on the idea that acts are omitted as a response to the perceived risk fear of punishment. This seminal paper helped to introduce routine activity theory to criminology.
It also has been used in conjunction with many crime control strategies including problem-oriented policing and problem analysis. Now women were in the work place changing the dynamic of the workplace which in turn led to more crime due to women no longer being in the home but roaming the streets. The theory has been extensively applied and has become one of the most cited theories in criminology.
This explanation assumes that crime results from a rational process in which offenders make decisions and choices often planning their criminal activity so as to maximize the benefits and. It also specifies the situational model that according to the theory explains the occurrence of crime events. It outlines the theorys basic assumptions about the role of routine activities in explaining a societys crime rates.
Cohen and Felson explained that crime rates could vary without actual changed in the number of potential offenders or offender motivation. Crime is a product of opportunity. Crime is offense - specific.
Routine Activity- If an opportunity is a necessary condition for crime to occur then crime can reduced by removing the opportunity to complete the act. Routine activity theory introduced by Cohen and Felson may be useful in informing social workers to design better interventions with juvenile offenders. How does rational choice theory dovetail with routine activities theory.
Classical theory also called R ational or Choice Theory is based on the early writings of Cesare Beccaria 17381794 and Jeremy Bentham 17481832. Both Choice and Trait theories are similar in nature because they both draw from an individuals mental process or behavioral upbringing. The routine activity theory suggests that crime requires three elements for it to take place.
Routine activity theory crime prevention Routine activity theory is one of the main theories of environmental criminology. The rational choice theory focuses on how people calculate the costs and benefits of committing a crime weigh the pros and cons and then chooses the option that yields the highest net benefits. The routine activity theory and rational choice theory are essential in the field of security.
The routine activities of Americans have led to a greater increase in crime. Much like Benthams hedonistic calculus this theory posits that offenders weigh the pros and cons of participating in the behavior to make a deci-sion. Post 1950s America when dual incomes became the norm.
The idea is that crime is the result of peoples everyday behavior of the way in which offenders and victims go about their daily lives. Rational Choice Theory- But in the end crime is not simply due to underlying motivation or predispositions. This study used Routine Activity Theory to explain delinquency based on the theorys three main components.
Crime is not something extraordinary that requires a deep psychological analysis. Routine activities theory is a subsidiary of rational choice theory. This theory was used by Cohen and Felson 1979 to explain the rising crime rates in the United States.
Cohen in their explanation of crime rate changes in the United States between 1947 and 1974. An accessible target 2. 5 Similarly routine activities theory.
Rational Choice Theory. One example of rational choice theory would be an adolescent who joins a gang. It is also involves a concrete choice.
-Argues that people are rational and pursue own interest in an attempt to maximize pleasure minimize pain. The absence of a capable guardian the existence of a motivated offender and a. Since gang activity is typically restricted to areas that experience poverty and other forms of social strain the.
According to Brantingham and Brantingham 1984 the level of risks is one of the factors that. Rational choice theory examines the choices of an offender and the influences that affect the decision to commit a crime such as morality risks and rewards. It was first proposed by Marcus Felson and Lawrence E.
If a criminal chooses an action that is likely to get them caught their gain from committing a crime will be negative. Routine activities theory is based on the idea that offenders make rational choices about whether to commit a crime. That could intervene The theory states that a crime occurs when the following three elements come together in any given space and time.
Developed by Cohen and Felson 1979 routine activities theory requires three elements be present for a crime to occur. Although at first glance this distinction may appear inconsequential it has important implications for the research and. Crime happens because of poverty.

Routine Activity Theory Oxford Research Encyclopedia Of Criminology

Comments
Post a Comment